nmea2000 – complete library for working with NMEA2000 bus
Constants
Functions
- nmea2000.isglobal(pgn)
Checks whether
pgndestination global or addressed.
- nmea2000.isfast(pgn)
Checks whether
pgnmessage is fast-packet or single-frame.
- nmea2000.isprop(pgn)
Checks if
pgnis a standardized NMEA Network Message or proprietary.
- nmea2000.packmask(pgn[, ...])
Pack specified PGNs into the most optimal filter (message ID and mask pair). Using packed masks instead of ‘accept all’ masks can improve Gateway performance See
pyb.CAN.setfilter()andNMEA2000.rxcallback().The returned mask may accept PGNs not specified in the parameter list, and the received PGN must be verified in the handler. Use this method only if all filter slots are used
- nmea2000.parseid(msgid, list=None)
Splits the message ID into it’s components:
PGN,destination address,priority,source address. If thePGNis global, thedestination addresswill always beBROADCAST.
- nmea2000.parsetag(proptag, list=None)
Splits proprietary tag into it’s components:
manufacturer code,industry group.This method is used to parse data from messages with proprietary PGN.
- nmea2000.buildpgn(pgn, destination=255)
Combines PGN and destination address into single value. Global PGNs can not be combined with destination address, so they are returned as is. This method can be used to construct NMEA0183
PCDINsentences. See alsoNMEA2000.buildid().
- nmea2000.buildtag(manufacturer, industry=4)
Combine manufacturer and industry codes into single proprietary tag. Can be used to construct proprietary PGNs.
- nmea2000.toraw(data, msgid, tx=False, time=-1, out=None)
Returns the CAN frame in RAW format. This format is used in Yacht Devices software and hardware products, and is described in Appendix E of the Yacht Devices Wi-Fi Gateway manual. See also:
pyb.CAN.test().
Classes
- class nmea2000.NMEA2000(can, setup=True, address=127, silent=False, loopback=False, cansleep=False, rtc=None)
Creates an NMEA2000 device on specified
CANinterface. NMEA2000 object uses FIFO0, FIFO1 can only be used directly by user code (e.g. to receive messages with 11-bit identifier).The
setupparameter is used to set the required CAN ‘receive-all’ filter on FIFO0 and to check the baud rate. If a baud rate mismatch is detected, an error is printed to REPL. To set the CAN filter manually, usesetup=Falseand add the following line after creating the CAN object:can.setfilter(0, pyb.CAN.MASK32, 0, (0, 0))
Set
cansleep=Trueto enter SLEEP state when CAN bus voltage drops below 7V. This can only happen if a USB power source is connected, because the Gateway shutdown threshold on the CAN bus is 9 volts.Note
Only one NMEA2000 object can be created per CAN interface.
After the device has been created, the address claim procedure is initiated to obtain a free address on the bus. The address is stored in the EEPROM for use the next time. The NMEA 2000 device can be used normally only 250 milliseconds after the address has been obtained. The Standard requires this to give devices time to claim their addresses.
 Initialization example
Initialization exampleimport pyb import nmea2000 can = pyb.CAN(1, baudrate=250_000) n2k = nmea2000.NMEA2000(can)
Default Received PGN list #
Name
PGN
Mandatory
1
ISO Acknowledgment
59392
No
2
ISO Request
59904
Yes
3
Transport Protocol
60160
No
4
60416
No
5
Address Claim
60928
Yes
6
ISO Commanded Address
65240
No
7
NMEA - group function
126208
Yes
8
System Time*
126992
No
9
GNSS Position Data*
129029
No
10
Local Time Offset*
129033
No
* used for time synchonization if RTC object is provided.
Note
Mandatory PGNs must be allowed by
CAN filtersto FIFO 0 for correct operation of NMEA2000 device.Default Transmitted PGN list #
Name
PGN
Interval
1
ISO Acknowledgment
59392
2
ISO Request
59904
3
Address Claim
60928
4
NMEA - group function
126208
5
PGN list - group function
126464
6
Heartbeat
126993
1 minute
7
Product Information
126996
8
Configuration Information
126998
Constants
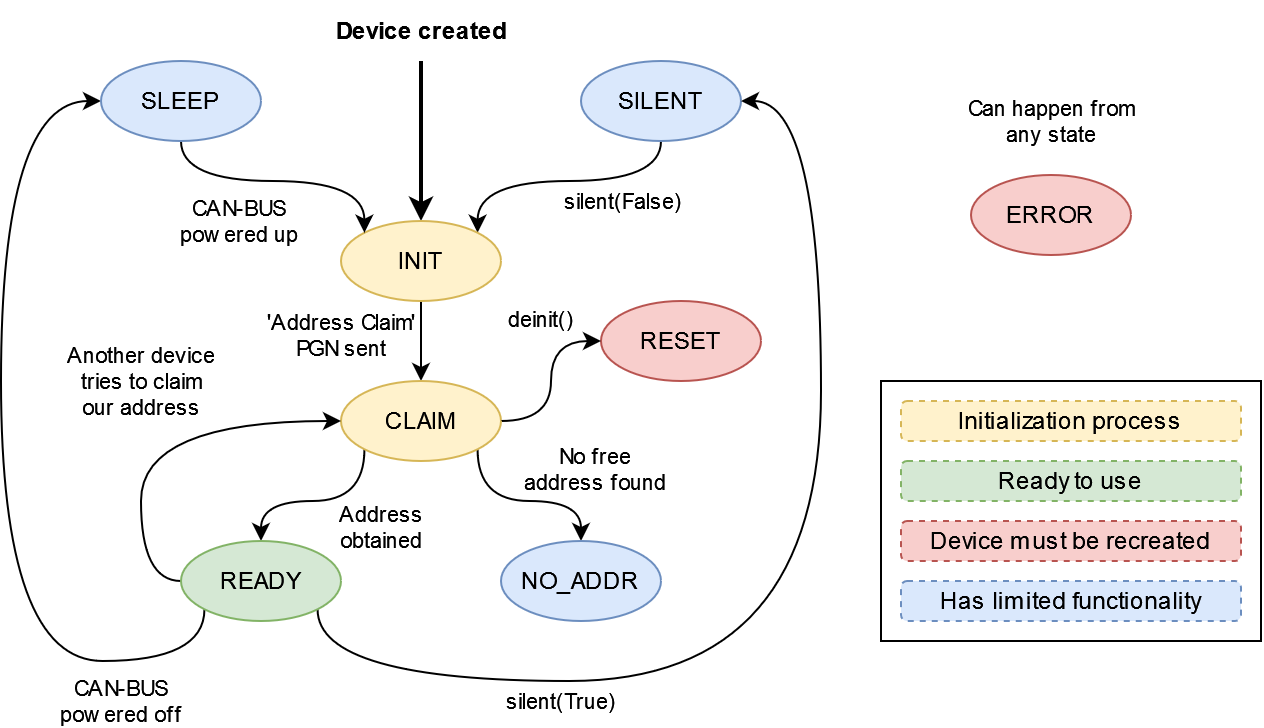
Device state constants Name
Value
Description
NMEA2000.RESET
0
Device is not initialized.
NMEA2000.SILENT
1
Device is in silent mode.
NMEA2000.INIT
2
Device initialization started.
NMEA2000.CLAIM
3
Device is claiming address.
NMEA2000.READY
4
Device is ready.
NMEA2000.NO_ADDR
5
Device can’t claim address (too many devices on the bus).
NMEA2000.SLEEP
6
CAN bus not powered. Device temporary in sleep mode.
Device will try to claim address after bus is powered up.
This state is possible if the NMEA20000 object was
created with cansleep=True.
NMEA2000.ERROR
7
Unknown error has occured.
Message type constants Name
Value
Description
NMEA2000.AUTO
0
Automaticaly detect message type based on PGN.
NMEA2000.SINGLE
1
Send as single-frame message.
NMEA2000.FAST
2
Send as fast-packet message.
‘Heartbeat’ PGN equipment state constants Name
Value
Description
NMEA2000.HB_OK
0
Normal operation.
NMEA2000.HB_FAULT
1
Something is not right.
NMEA2000.HB_RESERVED
2
Undefined
NMEA2000.HB_NA
3
Data not available.
Class methods
- rtc([rtc])
If the
pyb.RTCobject is linked to NMEA2000, the system time is automatically synchronized when PGN 126992, 129029 and 129033 are received.
- state()
-
- Returns:
Current state of NMEA2000 device.
- Return type:
- silent([silent])
Enable or disable silent mode of NMEA2000 device.
In silent mode, the NMEA2000 device will not respond to any request or command received from the bus. Automatic transmission of PGNs (e.g. periodic transmission of ‘heartbeat’ PGN) is also disabled. However, you can still manually receive and send NMEA2000 messages.
- loopback([loopback])
Enable or disable forwarding of sent messages back to the internal NMEA2000 device. If enabled, any sent message will be processed by the Gateway’s internal code as it was received from the bus. Forwarded messages will not trigger an
rxcallback().If disabled, the address claim request sent by the user program will be processed by all devices on the bus except the Gateway. If enabled, the Gateway will process the message and send a response which will trigger
pyb.CAN.txcallback().
- cansleep([cansleep])
Enables or disables the ability to enter
SLEEPstate.
- assemble([assemble])
Enables or disables the assembly of fast-packet messages before calling
rxcallback(). If disabled,rxcallback()is called for every CAN frame. Default state isTrue.
- address([address])
Sets or return the address for NMEA2000 device. When the address is set, device starts address claim procedure. It can be postponed with the
silent()method.
- reset_settings()
Resets changes made by
address_claim(),product_info()andconfig_info()methods.Equivalent to YD:RESET command.
Note
Don’t use too often. It may cause excessive wear of internal EEPROM.
- address_claim([unique=-1, mfc=717, dev=0, devfunc=135, devclass=25, sys=0, industry=4, selfcfg=True])
Sets or returns fields for PGN “ISO Address Claim”. Here you can change the device type (see example). Updated values are stored in EEPROM and restored after a restart.
- Parameters:
unique (int) – Unique number to set. Range: [0..2097151]. Negative values replaced with default Gateway’s unique number.
mfc (int) – Manufacturer code to set. Range: [0..2047].
dev (int) – Device instance to set. Range [0..255].
devfunc (int) – Device function to set. Range: [0..255].
devclass (int) – Device class to set. Range: [0..127].
sys (int) – System instance to set. Range: [0..15].
industry (int) – Industry group to set. Range: [0..7].
selfcfg (bool) – Self configurable flag to set.
- Returns:
Current values of the PGN “ISO Address Claim” fields if no parameters are specified.
- Return type:
- product_info([dbver=3000, code=9765, modelid=None, swver=None, modelver=None, modelserial=None, certlevel=2, len=2])
Sets or returns fields for PGN “Product Information”. Updated values are stored in EEPROM and restored after a restart.
- Parameters:
dbver (int) – Database version to set. Range: [0..65535].
code (int) – Product code to set. Range: [0..65535].
modelid (str or bytes) – Model ID to set.
Nonewill be replaced with the default Gateway model ID. Max length – 32.swver (str or bytes) – Software version to set.
Nonewill be replaced with the current Gateway firmware version. Max length – 32.modelver (str or bytes) – Model version to set.
Nonewill be replaced with the default Gateway model version. Max length – 32.modelserial (str or bytes) – Serial number to set.
Nonewill be replaced with the serial number of the Gateway. Max length – 32.certlevel (int) – Certification number to set. Range: [0..2].
len (int) – Load equivalancy number to set. Range: [0..255].
- Returns:
Current values of the PGN “Product Information” fields if no parameters are specified.
- Return type:
tuple(int, int, bytes, bytes, bytes, bytes, int, int) or None
- config_info([install1=None, install2=None, mfc=None])
Sets or returns PGN ‘Configuration Information’ fields. Accepts UTF-8 encoded strings. It is possible to set the callback on change of installation description strings, see example.
If provided strings contain non-ASCII characters, they are internally converted to UTF-16. UTF-16 encoding always uses 2 bytes to represent a single character, so the maximum length of the string is halved.
- Parameters:
install1 (str or bytes) – Installation Description 1 to set.
None– don’t change current value. Max length: 70 (ASCII), 35 (UTF-8).install2 (str or bytes) – Installation Description 2 to set.
None– don’t change current value. Max length: 70 (ASCII), 35 (UTF-8).mfc (str or bytes) – Manufacturer information to set.
None– don’t change current value. Max length: 70 (ASCII), 35 (UTF-8).
- Returns:
Current values of the “Configuration Information” PGN fields if no parameters provided.
- Return type:
- equipment([equipment])
Set device status for NMEA2000 device. See device status constants.
The device status is sent to the bus every minute using the ‘Heartbeat’ PGN, so it may take up to a minute to get an updated status on the bus. The transmission interval of this PGN can be changed using the YD:PGN command.
Callbacks
- statecallback(callback)
Register callback on NMEA2000 device state change.
callbackmust accept 2 parameters:NMEA2000 objectand state ID.
- reqcallback([callback, all=False])
callbackwill not be called on request of ‘Address Claim’, ‘Product Information’ and ‘Configuration Information’ PGNs addressed to this unit’s address. These calls are handled by the NMEA2000 object, but can be received withrxcallback()if necessaryIf request is addressed to device and callback returns None or False, then NACK state will be sent using ‘ISO Acknowledgment’ PGN.
callbackmust accept 4 parameters:NMEA2000 object,requested pgn,destination addressandsource address.
- rxcallback(index[, callback, pgn=None, dst=None, prio=None, src=None, mask=None])
Register a callback to receive NMEA2000 messages. Up to 16 callbacks can be registered. Each callback (starting with index 0 and in ascending order) is compared with the received message on match and called sequentially until one of the callback functions returns False or True. See code examples.
The callback can be set for a single PGN, by sender or destination address, or for the group of messages using the mask parameter applied to the message ID. The callback function must have 4 parameters:
NMEA2000 object,received data,message IDandsequence number. For single frame messages, the sequence number is set to -1.The callback can also be set to:
None– removes callback at specified index;False– blocks message from calling next callback in list;True– reserved for future use, currently works the same as False.
The callback can return None or something that can be evaluated as False or True:
None– pass received message to next callback in list;False– block message from calling next callback in list;True– reserved for future use, currently works the same as False.
- Parameters:
index (int) – Callback index (priority). Range: [0..15].
callback (function(NMEA2000, bytes, int, int) or None or False or True) – Function to be called when message is received.
pgn (int) – PGN acceptance filter.
dst (int) – Destination address acceptance filter. Can not be used with global PGNs.
prio (int) – Message priority acceptance filter.
src (int) – Source address acceptance filter.
mask (tuple(int, int) or list(int, int)) – Message ID acceptance filter. If set, overrides
pgn,dst,prioandsrc.
- cfgcallback(callback)
Register callback on external modification of PGN ‘Configuration Information’ installation description strings, see
config_info(). This callback allows commands or configuration data to be sent to the user program over the CAN bus, see example.callbackmust accept 3 parameters:
Message transmission
- buildid(pgn, destination=255, priority=6, source=255)
Assemble message ID from specified fields.
- Parameters:
pgn (int) – NMEA 2000 PGN.
destination (int) – Destination address to send message to. Range: [0..251] or
BROADCAST.priority (int) – Message bus priority. Range: [0..7].
source (int) – Source address to send message from. Range: [0..251] or
BROADCAST. If source isBROADCAST, then it will be replaced with current deviceaddress().
- Returns:
Assembled message ID.
- Return type:
- send(data, id, seq=None, type=AUTO, timeout=0)
Send NMEA 2000 message. Automatically detects message type (fast packet or single frame) based on
idand sends in correct format.Global sequence number will be used for fast packet messages if
seqis not specified. So you don’t need to store a separate sequence number if your program only sends a single fast-packet PGN.To send CAN frames with 11-bit identifier, use
pyb.CAN.send().- Parameters:
- Returns:
Unique number of sent message in TX queue. See
pyb.CAN.txcallback().- Return type:
- sendpgn(data, pgn, dst=255, prio=6, src=255, seq=None, type=AUTO, timeout=0)
Send NMEA 2000 message. Equivalent to
send(data, buildid(pgn, destination, priority, source), seq, type, timeout)Message sending examplebin_status = bytearray((7, 0xF1, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF)) # send 'Switch Bank Status' with bank 7 and first two channels enabled. _ = n2k.sendpgn(bin_status, 127501)
- request(pgn, destination=255)
Request
pgnfrom other NMEA2000 devices using ‘ISO Request’ PGN. Useloopback()if you want the Gateway to process the request as well.